If you’re concerned about data security and privacy, you may have heard of encryption for communication applications, even if only in a superficial way.
In addition, it is possible that your interest in the subject arose as a result of some news of a leak or theft.
This is a reality that has been growing in recent years. We are increasingly concerned about our information and technology has a direct impact on our routines.
Who would have thought, for example, that the cell phone would become so important to us? But not because of its original functionality, making and receiving calls, since messaging apps have practically doomed phone calls.
Do you have any idea how many messages have been received and sent in the last few hours via the main tools of this type? And how many have replaced a connection?
Thousands of messages every day
Brazilians send thousands of messages every day to friends, family, work colleagues and other people. In the world, an average of 55 billion messages are sent every day via WhatsApp.
Even services like WhatsApp have become strategic for businesses. Considered sales tools, messaging apps help many entrepreneurs to boost the economy.
Because of this importance, we want the messages to remain restricted to interested parties only. These are often private conversations that deal with personal and strategic matters.
Given the frequency with which we all use these tools, it is increasingly important to protect privacy and personal information.
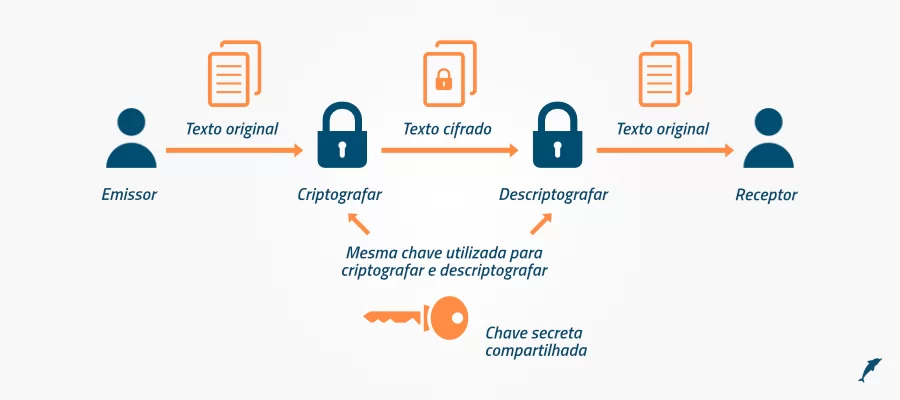
One way of doing this is by using encryption for communication applications.
Definition of cryptography
Before looking at who adopts encryption for end-to-end communication applications, it’s worth remembering the basic concept behind secure messaging.
Security systems for communication have existed for centuries. Basically, the idea is to get a message or information to a destination without any unauthorized person being able to read it.
In practice, with the help of the internet, we send a lot of private data to other computers or servers every day.
Encryption takes your data and scrambles it, making it impossible for anyone who intercepts it to read or understand.
When it reaches the recipient, the data is decrypted back to its original form so that it can be read and understood.
Unencrypted data is called plain text and encrypted data is called cipher text.
The way a device takes data and encrypts it is called the encryption algorithm. It is used with a cryptographic key, so that only the person with the right key can decrypt it.
For example, if we wanted to encrypt the message “good morning!” and send it to someone else, we would need to use an encryption algorithm, which would encrypt it to something like “SZKKB YRIGSWZB”. That way, someone using the same technology could open it and read it.
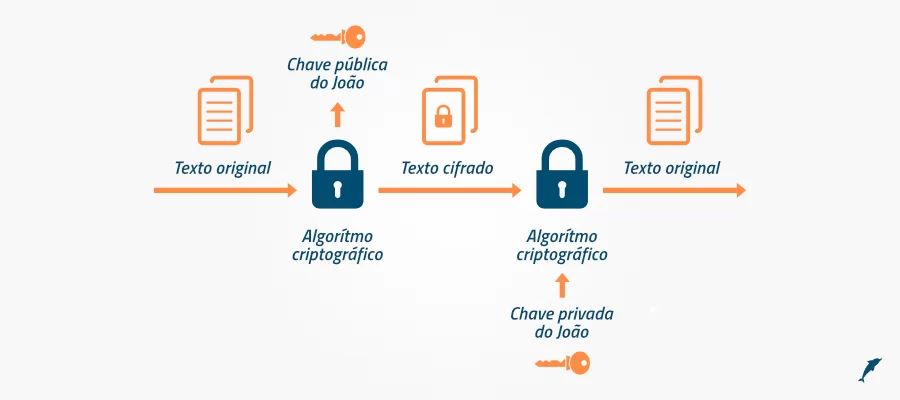
From end to end
End-to-end encryption is asymmetric. It protects the data by ensuring that only two people can read it: the sender and the recipient.
This means that no one else can read the data, such as hackers, governments, companies or servers. Therefore, when a user sends a message to another, even if it has been intercepted, it cannot be read.
If the message passes through WhatsApp’s server, for example, it won’t be able to read it. If the service wanted to provide this data to third parties, they would not be able to do so.
This is what happens when encryption for communication applications is end-to-end. To find out more about how WhatsApp messages are encrypted, as well as the algorithms used, click here.
Encryption for communication applications is a standard
The use of encryption in communication applications has become a standard in recent years. However, it has not yet been adopted by all manufacturers.
In fact, encryption is not mandatory in all situations, but in some you definitely use it, such as when you buy items online and enter your card details.
At times like these, encryption happens without you knowing. In everyday life, you can opt for encryption for communication applications just to have the peace of mind of knowing that absolutely no one else can access your messages or calls.
End-to-end encryption means that unauthorized people won’t be able to access your data and your privacy is preserved.
|
|
Which applications to use
There are so many options on the market that it’s hard to say which is the best. Instead, we’ll list the most popular ones that use encryption for communication applications by default.
Encryption on WhatsApp
WhatsApp already has more than 1.5 billion users and integrates the encryption protocol into its conversations. This means that WhatsApp messages are end-to-end encrypted by default.
It has chat, group calls, file sharing, archiving, location sharing, broadcasting and much more.
The popularity of the app also works in your favor, as you probably won’t need to convince other people to download it.
WhatsApp is free to use and ad-free. However, it is owned by Facebook, which openly admits to collecting a lot of data about you for marketing purposes.
Encryption in Facebook Messenger
According to one BBC reportFacebook Messenger also uses encryption, but a little differently from the encryption used in WhatsApp, in which the message is encrypted from the sender to the server, which opens the message and encrypts it back to the sender end-to-end, the same signal protocol used by WhatsApp.
But there are already plans to implement the same end-to-end encryption on Facebook Messenger as is used on WhatsApp. Ultimately, this means that your messages cannot be viewed by the social network team.
Facebook Messenger also uses encryption, but a little differently from the encryption used in Whatsapp, in which the message is encrypted from the sender to the server, which opens the message and encrypts it back to the sender. end-to-end, the same signal protocol used by WhatsApp.
But there are already plans to implement the same end-to-end encryption on Facebook Messenger as is used on WhatsApp. This means that your messages cannot be viewed by the social network team.
Facebook Messenger works like most other apps, with group chat and calls, file sharing, location sharing and video calls. It’s also very easy to use, with stickers, GIFs and even games.
However, the application is owned by Facebook, which means that it still contributes to the data collected about you and billions of other users.
Encryption in Telegram
Telegram was one of the first apps on the market. End-to-end encryption is not active by default: you need to make sure that secret mode is active so that no one else can access your messages.
The app has features such as group chat, sending files and photos – also encrypted only in secret mode – missing messages, archiving functionality and voice and video calls.
When secret mode is active, messages can also self-destruct on all devices in a chat and there is the option to self-destruct your account within a set time.
Telegram is free to use and ad-free. All data is encrypted and stored on servers, except for secret chat messages.
Encryption in iMessage and FaceTime
Apple has introduced end-to-end encryption for all your messages in iMessage, the default app on iOS devices, and all FaceTime calls and videos.
iMessage and FaceTime are available on iOS mobile devices as well as Mac computers.
Both apps cover a range of basic functionalities, such as messaging, location or file sharing and voice and video calls. iMessage messages are backed up in iCloud, but this can be disabled in your settings.
Make sure you read the data privacy policies of all the applications you use. Make sure you are comfortable with them before trusting your chosen tool.
Sobre a Eval
EVAL has been developing projects in the financial, health, education and industry segments for over 18 years. Since 2004, we have offered Authentication, Electronic and Digital Signature and Data Protection solutions. Currently, we are present in the main Brazilian banks, health institutions, schools and universities, and different industries.
With value recognized by the market, EVAL’s solutions and services meet the highest regulatory standards of public and private organizations, such as SBIS, ITI, PCI DSS, and the General Data Protection Law (LGPD). In practice, we promote information security and compliance, increase companies’ operational efficiency, and reduce costs.
Innovate now, lead always: get to know Eval’s solutions and services and take your company to the next level.
Eval, safety is value.