Post-quantum cryptography, or post-quantum-
cryptography (PQC),
helps to mitigate cyber attacks.
Although 73% of organizations recognize that quantum computing poses a threat to traditional cryptography,
61% have not yet defined a strategy for a post-quantum world.
.
And 62% have five or more key management platforms, making PQC preparation a major challenge.
If organizations neglect their strategy, it will inevitably wreak havoc on their datacenters and put their most sensitive data at risk. Furthermore, transforming a company’s cryptography into post-quantum cryptography takes time.
Therefore, organizations around the world must test their applications, data and ecosystem devices that currently rely on traditional cryptography to ensure minimal disruption when quantum secure protocols become mandatory.
Why PQC now?
By 2024, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) intends to publish and standardize PQC algorithms so that organizations can be protected against quantum computing attacks.
As soon as NIST officially standardizes them, government
government bodies around the world
(BSI, ANSSI, etc.) will issue
compliance mandates
based on NIST’s PQC standardization process.
The institute is already holding conferences aimed at discussing the various aspects of the algorithms, both those selected and those being evaluated, in order to obtain feedback and inform decisions on standardizations.
They are already at the 5th conference, which was held from April 10 to 12 in Rockville, Maryland (USA).
Source: Unsplash – Michael Dziedzic
What is a quantum computer? It’s not science fiction. They exist.
As our subject is post-quantum cryptography, it is necessary to discuss quantum computing. In other words, the quantum computer, a device that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to process information.
One of the most promising applications of quantum computers is the
simulating the behavior of matter down to the molecular level
. They are already used for scientific research and advances in
medical
and vehicles, for example.
But a major concern related to them is their use by cybercriminals. They will act as a weapon to decrypt sensitive data and leave companies vulnerable.
And how are you preparing for this scenario?
Post-quantum cryptography
could weaken the HTTPS web protocol that encrypts the data we use and receive over the internet.
Today, machines are evolving rapidly and in less than 10 years’ time it will be possible for a hacker to use a quantum computer.
Consequently, hacking and decrypting data that would be impossible or take billions of years.
QUIBITS: The structure of the quantum computer
While a conventional computer operates with the binary system, using only zeros and ones, quantum
quantum computers use qubits to encode data
. One qubit is a mixture of all values between zero and one, which allows it to represent not only zero and one, but also a linear combination of the two.
They are like subatomic particles, such as electrons or photons. They have distinct quantum properties, which implies that an interconnected set can offer significantly higher processing capacity compared to the same amount of binary bits.
Among these characteristics, superposition stands out, while another is called entanglement.
Rather than being reserved for science fiction films, quantum computers exist today as organizations move towards commercialization.
Check it out:
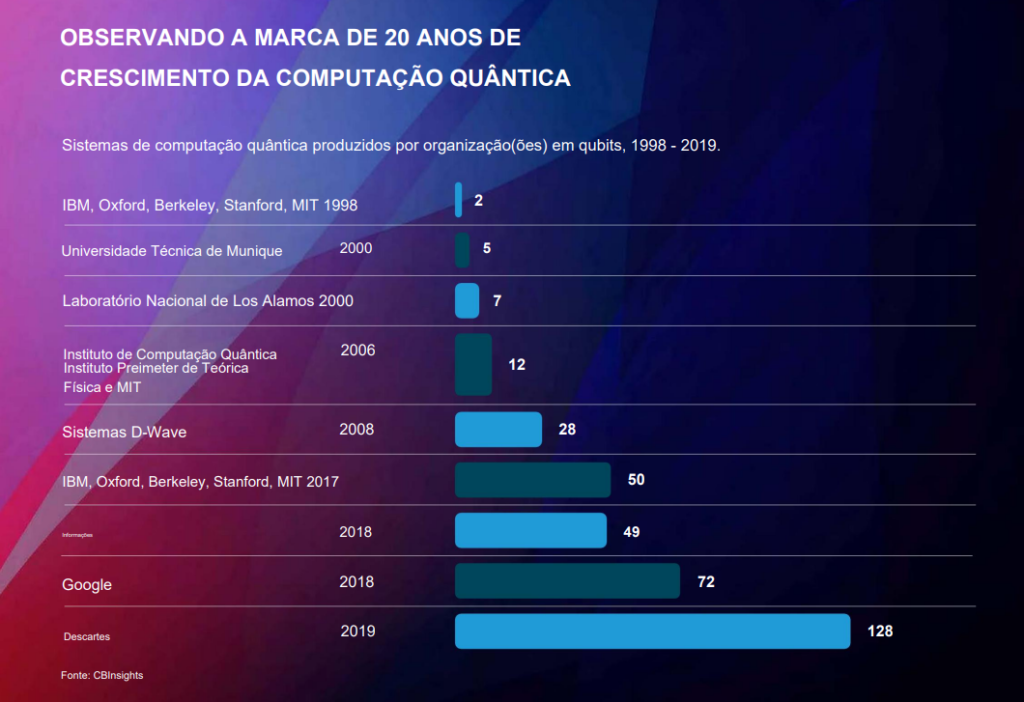
- O
Google Sycamore computer
has
70 qubits (quantum bits)
– August 2023. - O
IBM Osprey quantum processor with 433 qbits
is the
most powerful in the world
and the company plans to reach the 4,000 qubit stage with its Kookaburra processor in 2025. - Technology companies such as
Google, IBM, Microsoft and Amazon
have announced
quantum computing available in the cloud
as a service.
What is Post Quantum Cryptography (PQC)?
Today’s public key cryptography is based on factoring for RSA algorithms or discrete log problems with DSA, Diffie-Hellman and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC).
A
Post Quantum Cryptography uses a new set of Quantum Resistant Algorithms
created by researchers and tested by industry standard bodies such as NIST and ANSSI, which are in the process of becoming part of compliance requirements.
It will therefore provide long-term protection for government and commercial data against the emerging threat of quantum computing. Quantum computers will make today’s conventional public key encrypted infrastructures insecure.
Using a hybrid encryption model, PQC allows customers to combine classical and quantum-resistant algorithms on a single platform, providing a secure transition to a post-quantum world.
What does the CISO need to know?
Know your crypto. Understand where the encrypted data is and what type of cryptography is used today, so it will be easier to plan for the use of post-quantum cryptography. A crucial point is to analyze where your organization currently uses encryption and what the impacts will be in the event of a security breach.




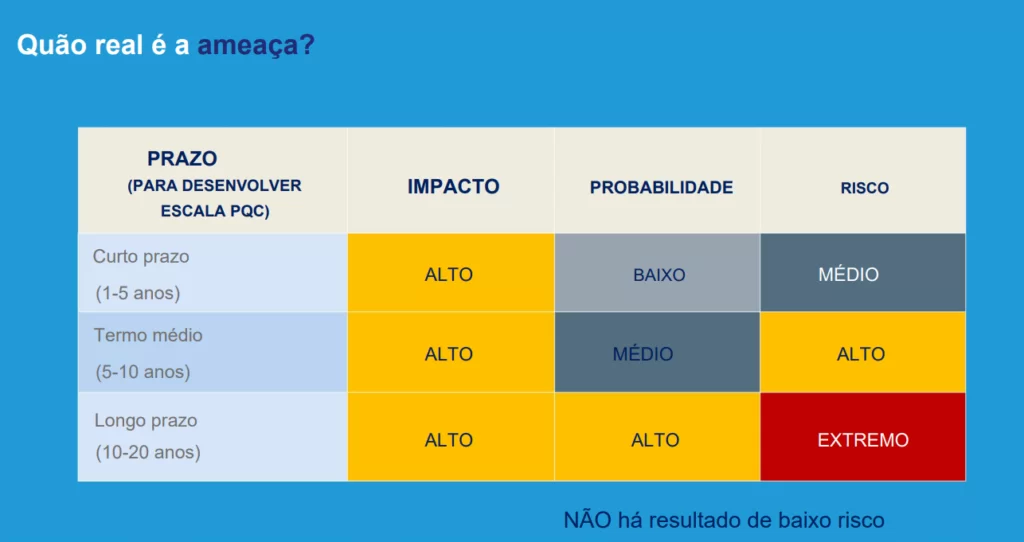
To prepare for Post Quantum Cryptography (PQC), it is important to assess the
level of risk exposure
and develop a plan to reduce it. One suggested strategy is to adopt solutions that combine conventional algorithms with quantum security methods.
So start the preparation process today,
reviewing the set of cryptographic algorithms in use
and assessing the organization’s overall readiness for the PQC era. Start planning a security architecture suitable for the quantum environment, including incorporating support for the new algorithms.
First of all, thoroughly examine all applications that handle sensitive information. If you had to change an algorithm, would these applications continue to work normally?
If not, what adjustments would need to be made to ensure it works? Do this analysis for each application that depends on encryption within the organization, in order to create a plan that guarantees the continuity of operations. Starting this process early will help ensure a smooth transition to protecting the organization’s data in the post-quantum world.
Conclusion:
- Complete the implementation of post-quantum algorithms in all the organization’s systems and applications.
- Carry out final validation tests to guarantee the integrity and effectiveness of the new algorithms.
- Document and communicate the results of the migration to all stakeholders, including employees, customers and business partners.
- These steps will provide a smooth and secure transition to post-quantum cryptography, ensuring the security of the organization’s data in the quantum computing landscape.
Webinar: Navigating post-quantum cryptography (PQC): Prepare for the future!
Check out the recording of the live that presents practical strategies and tactical execution to deal with the challenges of post-quantum cryptography.
Thales High Encryption Speed (HSE) Solution – Quantum Defenses
O
NIST recommends a hybrid approach
to cryptography, using crypto-agile platforms for a smooth transition.
In practice, this means:
- QKD – Use quantum mechanics to establish and distribute keys
- Algorithms – Support for alternative modes with classic algorithms and QRA
- RNGs – Combine QRNGs with NIST certification
Hybrid encryption refers to the use of proven classic encryption algorithms. And quantum-resistant encryption algorithms. Hybrid encryption requires a cryptographic platform and guarantees long-term data protection in a post-quantum world.
As such, high-speed encryption can help protect many environments, including:
- Data center interconnection
- Financial services
- Government
- Critical National Infrastructure
O
Thales HSE has the ability to quickly modify cryptographic primitives
and has flexible upgradeable technology without built-in obsolescence. This ensures that organizations can adapt quickly in a constantly evolving cybersecurity landscape.
Check out the benefits:
- Total separation of cryptographic security tasks.
- Compatible with external entropy sources.
- Field-programmable FPGA encryption engine.
- Ready for Quantum (compatible with QKD).
- Supports CFB, CTR and GCM encryption modes.
- Self-correcting key management.
- Support for 128-bit and 256-bit AES algorithms.
About the Eval Digital and Thales partnership
The partnership between Eval and Thales represents a strategic alliance to offer cutting-edge technological solutions. Together, these companies combine expertise and innovation to meet market demands with excellence.
The combination of Eval Tecnologia’s resources and Thales’ experience results in robust and secure solutions capable of tackling the most complex challenges.
And all that’s missing from this partnership is your company. So ensure data protection on the move.










