“Cryptographic flaws have become a growing problem in a world heavily dependent on digital transactions and online communications that make use of cryptography.
In this context, cyber security, with a special focus on cryptographic algorithms, has become critical. These algorithms are an essential tool for protecting sensitive data.
However, the effectiveness of this data encryption is directly dependent on its correct and secure implementation, an aspect that, unfortunately, is often overlooked.”
A
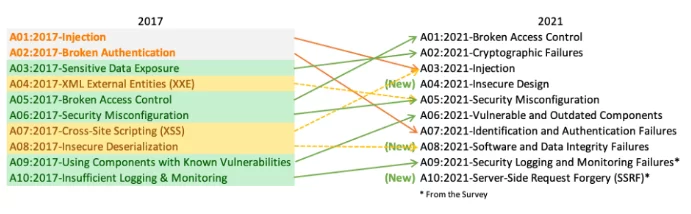
OWASP (Open Worldwide Application Security Project)
) is a non-profit foundation that works to improve software security. In 2021, the foundation published its latest “Top 10” list,
a ranking of cybersecurity threats
.
On this list,
cryptographic flaws have risen to second position
highlighting the seriousness of this problem.
Previously categorized as “Exposure of Sensitive Data,” cryptographic flaws have been recognized as the root cause of many security breaches.
These are not mere symptoms of broader security problems, but fundamental flaws that allow sensitive data to be exposed and systems to be compromised.
This paper will explore the growing threat of cryptographic flaws and highlight the importance of tighter control over cryptographic keys and algorithms.
By understanding the nature of these flaws and implementing appropriate controls, we can make our systems more secure and better protect our data from cyber threats.
The need for stricter control over Cryptographic Keys and Algorithms
In short, encryption is a powerful tool for protecting sensitive data, but when misused or neglected, it can be the source of catastrophic security breaches.
Many of the most common mistakes related to cryptography can be attributed to flaws in the control of cryptographic keys and algorithms. Here are some of the most common problems:
-
Use of weak or obsolete cryptographic algorithms and protocols
As technology advances, algorithms and protocols that were once considered secure can become vulnerable. For example, hash functions such as MD5 and SHA1 were once widely used, but are now considered insecure and are discouraged.
Similarly, the use of obsolete cryptographic padding methods, such as PKCS number 1 v1.5, can also lead to vulnerabilities.
-
Improper use of cryptographic keys
Cryptographic keys are a fundamental part of cryptography, but are often mismanaged.
Common problems include the use, generation or reuse of weak cryptographic keys, and lack of proper key rotation.
In addition, improper storage of keys, such as storing keys in source code, can make them vulnerable to exposure and theft.
-
Plain Text Data Transmission
Even with encryption in place, if data is transmitted in clear text (e.g. via protocols such as HTTP, SMTP, FTP), it can be intercepted and read by attackers.
-
Failure to properly validate certificates and chains of trust
To establish a secure connection, you must properly validate the server’s certificates and trust chains. If you don’t do this, attackers can impersonate trusted entities and intercept or alter data.
-
No authenticated encryption
Authenticated encryption is a form of encryption that not only protects the confidentiality of data, but also its integrity and authenticity.
If only encryption is used, without authentication, the data can be vulnerable to certain types of attacks.
In practice, to mitigate these flaws, strict control over cryptographic keys and algorithms is vital.
Strengthening Cybersecurity: Mitigating Cryptographic Breaches
Cryptographic flaws, although dangerous, are avoidable. There are several preventive measures that can be taken to minimize the risk of such failures. Here are some of the most important ones:
-
Classify your data
Identify which data is sensitive and needs extra protection. This can include personal information, health records, credit card numbers, trade secrets, and any data that is subject to privacy laws or regulations.
-
Minimize storage of sensitive data
In other words, don’t store more than necessary. Discard sensitive data as soon as it is no longer needed.
If you need to store sensitive data, make sure it is encrypted.
-
Use secure and up-to-date algorithms and protocols
Avoid using cryptographic algorithms and protocols that are known to be insecure or have become obsolete. Make sure that you are using algorithms and protocols that are considered secure by today’s cyber security authorities.
-
Implement effective key management
Cryptographic keys must be generated and stored securely, avoiding reuse between different systems or applications. In addition, a process must be implemented to rotate the keys regularly.
-
Use encryption in transit and at rest
Data must be encrypted, even at rest or when being transmitted between systems (in transit).
-
Authenticate your encryptions
Always use authenticated encryption, which protects not only the confidentiality of data, but also its integrity and authenticity.
-
Avoid obsolete cryptographic functions and schemes
Avoid using obsolete hash functions like MD5 and SHA1 and obsolete cryptographic padding schemes like PKCS number 1 v1.5.
By adopting these preventive measures, organizations can strengthen their cybersecurity and mitigate the risk of cryptographic flaws.
Cyber security is a constantly evolving field, and it is important to always be vigilant and up-to-date with the latest and best practices.
Rise of Cryptographic Flaws: the urgency of strict control
As web security threats continue to evolve, it is essential that encryption practices evolve as well.
Implementing robust preventive measures and maintaining tight control over cryptographic keys and algorithms is a crucial step in ensuring data security and system reliability.
Raising awareness about the importance of secure and effective encryption is the key to combating the rising tide of cryptographic flaws.
Eval leads in Cryptographic Agility and Advanced Technologies
Eval is a company that differentiates itself in the market by adopting and offering advanced technologies. One of its main areas of expertise is cryptographic agility, along with electronic signature tools, essential in today’s digital age.
Eval’s electronic signature solutions are robust tools that provide the level of security required for digital transactions and agreements. With them, the authenticity of documents, contracts, and digital transactions can be confirmed, protecting against fraud and misunderstandings.
However, it is in cryptographic agility that Eval really shines. As one of the most vital strategies for protecting digital information, cryptographic agility enables rapid adaptation to threats and evolutions in the cybersecurity landscape.
Cryptographic agility is essential for maintaining trust in digital environments, where threats are always evolving and data security is of utmost importance. Eval recognizes this need and is at the forefront of implementing systems that enable rapid change and updating of cryptographic algorithms and security protocols.
At Eval, we use the latest and most secure forms of encryption and cryptographic agility practices to ensure that our customers’ data is always protected, without compromising the ability to adapt to the changing digital security landscape.
Contact Eval to learn more
Now that you are aware of the growing threat of cryptographic flaws and the importance of strict control over cryptographic keys and algorithms, it is time to take a step further.
Don’t leave the security of your data to chance. Effective protection of your data starts with choosing a reliable and experienced technology partner.
To learn more about how Eval can help you strengthen your data security and reduce the risks associated with cryptographic flaws, contact us today. Our experts are ready to listen to your needs and work out a customized solution that best meets your requirements.
Don’t wait until it is too late. Make securing your data a priority today, and find out how Eval can help you achieve this.
Contact Eval now and take the first step toward a safer future.
About Eval
With a track record of leadership and innovation dating back to 2004, Eval not only keeps up with technological trends, but we are also in an incessant quest to bring news by offering solutions and services that make a difference to people’s lives.
With market recognized value, Eval’s solutions and services meet the highest regulatory standards for public and private organizations, such as SBIS, ITI, PCI DSS, and LGPD. In practice, we promote information security and compliance, increase companies’ operational efficiency, and reduce costs.
Innovate now, lead always: get to know Eval’s solutions and services and take your company to the next level.
Eval, safety is value.
Written by Arnaldo Miranda, Evaldo. Ai, reviewed by Marcelo Tiziano and designed by Caio.