In today’s digital landscape, data security has transcended necessity to become an obligation.
Every day, millions of transactions take place online, each of which requires a high level of cybersecurity in companies to protect valuable information.
In this context, Cipher Suites have emerged as crucial elements in building a secure digital environment. They form the backbone of many data security operations on the Internet, ensuring that information moves safely and efficiently.
This article seeks to explore the complexity of Cipher Suites, unraveling their nature, functioning and the importance they have in online data security.
What are Cipher Suites?
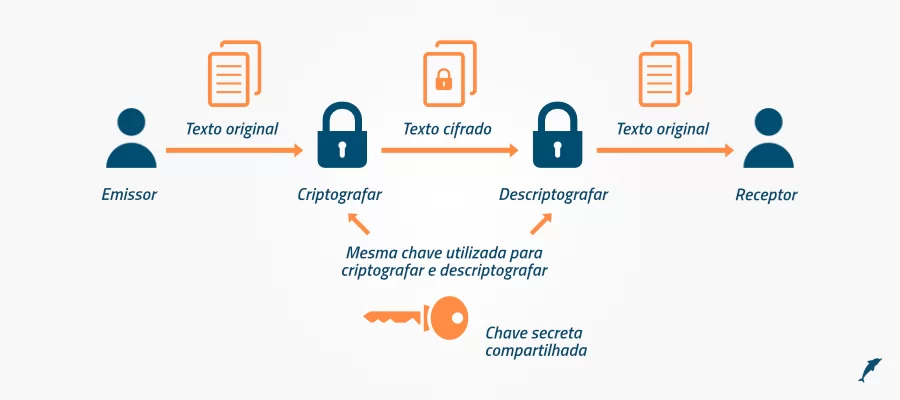
Cipher Suites is the set of algorithms used in combination to establish a secure connection, which include:
A session key algorithm and its key size:
This is the symmetric encryption algorithm used to encrypt the data transmitted in the session, such as 128-bit AES, for example.
A public key algorithm and its key size:
This is the asymmetric encryption algorithm used to encrypt the session key, such as 2048-bit RSA, for example.- A hash algorithm: It is used to guarantee data integrity, ensuring that data is not altered in the exchange of information. An example of a hash algorithm used is SHA.
- A key exchange algorithm: This is the method by which the session key is exchanged. The most common examples are RSA or Diffie-Hellman.
As a result, we have a constant that indicates which algorithms were used in a given session, such as “TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA”, which uses the TLS protocol, with the RSA asymmetric encryption algorithm, AES CBC 256 as the session key and SHA to guarantee data integrity.
Another example is“TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384“, which uses ECDHE for the key exchange, ECDSA for authentication, AES with 256 bits in GCM mode for encryption and SHA384 for the hash function.
Now that we understand that, let’s examine how Cipher Suites work in conjunction with HTTPS/TLS.
Another example is
“TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384”
which uses ECDHE for the key exchange, ECDSA for authentication, AES with 256 bits in GCM mode for encryption and SHA384 for the hash function.
Having understood this, let’s now see how they work together with HTTPS/TLS.
How does the technology work?
Cipher Suites are the driving force behind the security of an HTTPS connection, although their operation may seem a little complex. At the heart of this operation is the SSL/TLS handshake process.
Let’s dive a little deeper into the concept to understand how Cipher Suites work.
- When a connection is initiated between a client (e.g. a browser) and a server, an SSL/TLS handshake process is triggered. This process is a series of steps that are carried out to establish a secure connection between the client and the server. This is where the Cipher Suites come into play.
- During this handshake, the client and server exchange a list of the Cipher Suites they support. These lists are compared to find a Cipher Suite that they both support.The server then has the responsibility of choosing the most secure and efficient Cipher Suite that both support to be used during the session.
- Once the Cipher Suite has been chosen, the client and server begin the key exchange process, which is governed by the key exchange algorithm present in the chosen Cipher Suite.Here, it is important to note that a session key is created and it is this key that will be used to encrypt and decrypt the data transmitted during the session.In addition, the encryption algorithm that will be used to encrypt the data transmitted between the client and the server is defined, as well as the hash or MAC function that will be used to guarantee the integrity of the data.
At the end of the handshake, the connection is established and data can be exchanged securely between the client and server using the algorithms defined by the chosen Cipher Suite.
This ensures that communications are protected from interception or modification by malicious third parties.
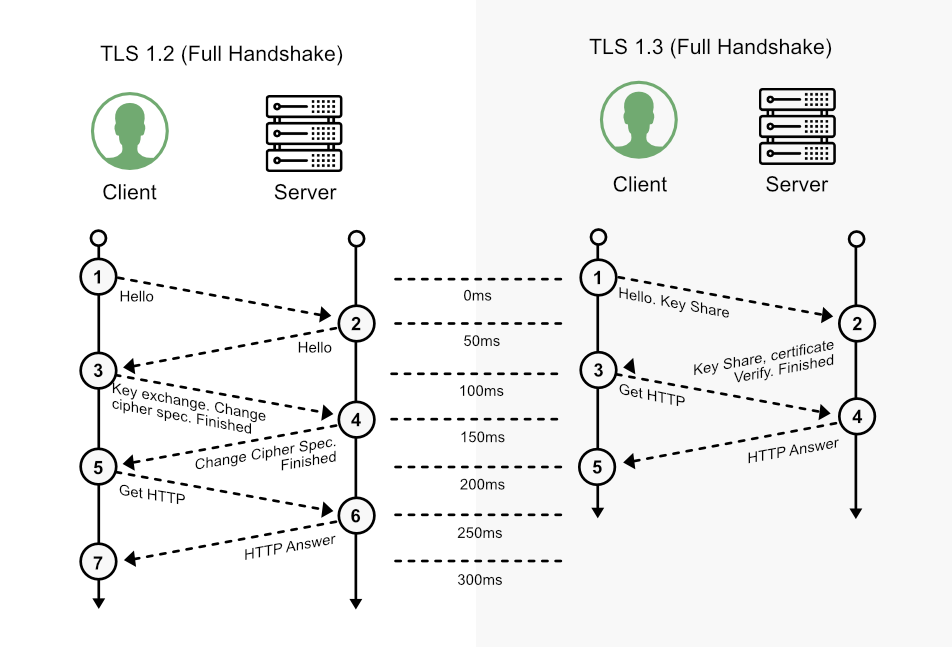
There are also some protocol variations, such as SSL, TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3. For educational purposes, below is a summary of the step-by-step TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3 protocols:
Why are Cipher Suites important?
Cipher Suites play a crucial role in setting up a secure HTTPS connection, as they encapsulate a variety of cryptographic functions, each playing a specific role in the security and integrity of the connection.
During the SSL handshake, the client and the web server use four main elements, each represented by a specific algorithm within the Cipher Suite:
- Key Exchange Algorithm:
This algorithm determines how the symmetric keys will be exchanged between the client and the server.
The symmetric keys are used to encrypt and decrypt the data transmitted during the session.
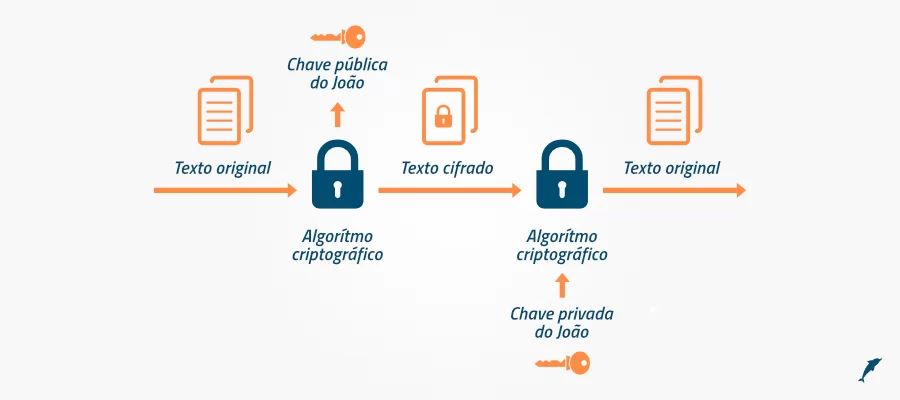
Asymmetric encryption algorithms used for key exchange include:
-
RSA:
Traditional and very well known, RSA is used in key exchange, in short, the recipient’s public key is used to encrypt a session key, which is a symmetric algorithm key, such as AES.
Diffie-Hellman (DH):
It is one of the best-known algorithms still used today for key exchange.
Diffie-Hellman Ephemeral (DHE):
This is a variation of DH, in which a new key is used for each new session.
Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH):
It is very similar to DH, but instead of using prime numbers, it makes use of elliptic curves.
Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman Ephemeral (ECDHE):
This is a variation of ECDH and DHE, in which a new key, using elliptic curves in this case, is used with each new session.
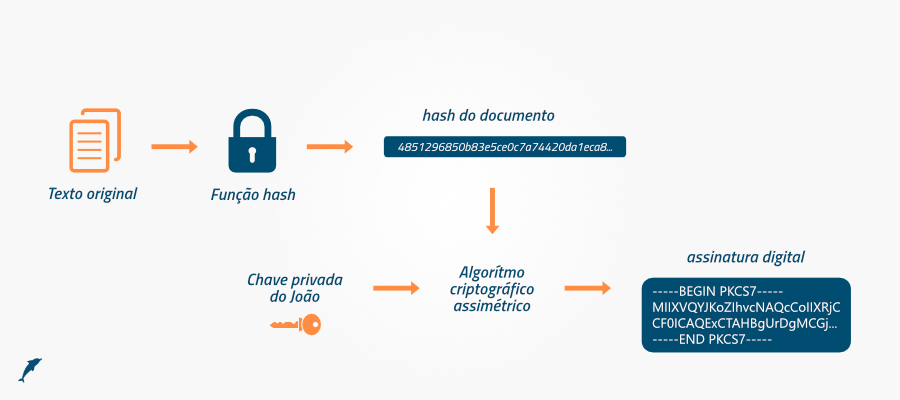
- Authentication Algorithm or Digital Signature:
This algorithm dictates how server authentication and client authentication (if required) will be implemented.
Authentication or Digital Signature allows the client and server to confirm each other’s identity, guaranteeing that they are communicating with the correct entity.
Authentication algorithms include RSA, ECDSA, and DSA.
- Symmetric encryption algorithms used for session keys:
This algorithm is used to encrypt the data that is transmitted between the client and the server during the session.
Symmetric encryption helps to guarantee the confidentiality of data at a low computational cost compared to asymmetric encryption algorithms, making it unintelligible to anyone who might intercept the communication.
Symmetric encryption algorithms include AES, CHACHA20, Camellia, and ARIA.
- Hash/MAC function:
This function determines how data integrity checks will be carried out. Data integrity is important to ensure that the data has not been altered during transmission.
Hash/MAC functions, such as SHA-256 and POLY1305, are used to create a unique checksum value for the data, which can be used to check whether the data has been altered.
These cryptographic functions are needed at various points in the connection to perform authentication, key generation and exchange, and a checksum to guarantee integrity.
To determine which specific algorithms to use, the client and the web server start by mutually deciding on the Cipher Suite to be used.
In practice, Cipher Suites are necessary due to the variety of servers, operating systems and browsers.
There is a need to accommodate all these combinations, which is why Cipher Suites are useful for ensuring compatibility.
The importance of Cipher Suites in data security
In practice, Cipher Suites play a vital role in data security in an increasingly digital world.
As we’ve seen throughout the article, they are the backbone of secure connections on the Internet, allowing information to be transmitted securely between clients and servers.
Cipher Suites provide a set of algorithms that guarantee authentication, privacy and data integrity during communication.
They help prevent a wide range of attacks, from the interception of communications to the manipulation of transmitted data.
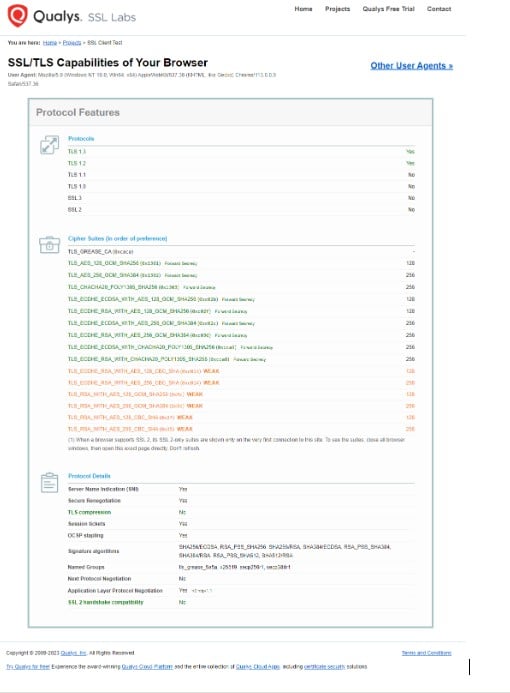
Given everything we’ve learned so far, there’s an interesting website on which it makes a diagnosis of which Cipher Suites your computer accepts.
To find out more go to:
https://clienttest.ssllabs.com:8443/ssltest/viewMyClient.html.
As a result, it should return something like:
As we can see, he has listed the protocols, the algorithms and some additional information. However, choosing the right Cipher Suites for a server is a crucial task for administrators.
Understanding technology is the first step to ensuring Data Security
An inappropriate choice can result in insecure connections, or even incompatibility with some clients.
Therefore, keeping up to date with the best practices for selecting Cipher Suites is an essential part of data security management.
And how do you do that? How do you choose the algorithms, remembering that they have to be accepted by both sides, the client and the server?
One way to increase your computer’s security is to eliminate some algorithms that are already known to be weak. To do this, we recommend reading Microsoft’s article in which they teach you the commands you can use via PowerShell to limit the use of weak algorithms.
Click here to see how to disable algorithms in Windows.
You can also check out the algorithms that are already accepted by default in Windows.
Click here to see more on windows 11
.
With the advance of technology and the constant evolution of security threats, it is crucial to understand the importance of Cipher Suites and how they work.
This knowledge will allow us to make more informed decisions to protect our data and keep our online communications secure.
In short, Cipher Suites are more than just a set of algorithms, they are the front line in the ongoing battle for data security on the internet.
About Eval
With a track record of leadership and innovation dating back to 2004, Eval not only keeps up with technological trends, but we are also in an incessant quest to bring news by offering solutions and services that make a difference to people’s lives.
With market recognized value, Eval’s solutions and services meet the highest regulatory standards for public and private organizations, such as SBIS, ITI, PCI DSS, and LGPD. In practice, we promote information security and compliance, increase companies’ operational efficiency, and reduce costs.
Innovate now, lead always: get to know Eval’s solutions and services and take your company to the next level.
Eval, safety is value.
Written by Arnaldo Miranda, Evaldo. Ai, reviewed by Marcelo Tiziano and designed by Caio.