The frequency of cyberattacks continues to increase, especially in the education, banking, healthcare and government sectors. This is why data encryption for cloud security has been a priority.
One reason for this increase is the transition from storing data in local databases to cloud storage, which is connected via wired and wireless technologies.
And data encryption for cloud security has been key in this transition phase.
While cloud platforms present a convenient way to store large databases containing customer, employee, financial and sales records, hackers can exploit weaknesses in cloud computing systems and gain unauthorized access by representing the package as local traffic.
Cybercriminals target organizations not only with on-premises data centers, but also those with environments hosted on cloud computing platforms.
Unfortunately, strong firewall rules are not enough to protect against cyber attacks and provide the necessary authentication and authorization for operational security protection against cyber attacks. Rigorous testing and validation of security at the database and application level is required.
It is crucial to protect data stored when at rest, where data remains on a device permanently, and in transit, and when it is moved from one location or network to another location/network.
To complicate matters, hackers use modern tools and techniques to gain unauthorized access to data within an organization, on the Internet or stored in cloud computing services.
Therefore, data encryption and authentication, implementation of SSL certificates and SSL connections are essential. Equally important is establishing policies that restrict unintended access to environments and regular identity validation and access management.
Realizing the benefits of authentication and data encryption for cloud security
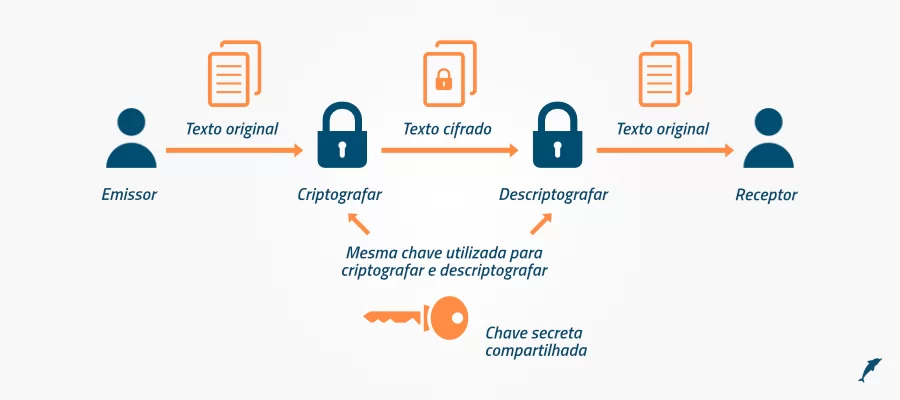
Basically, data encryption for cloud security protects sensitive and private informationby mixing blocks of text data into a secret code. A decryption key is required to decode the encryption.
Different algorithms, including DES, AES and RSA, transform the data into an unreadable format called ciphertext. The ciphertext is transmitted to the receiver with public and private decryption keys to decrypt the data.
The receiver decrypts the ciphertext using both keys to transform it into a readable format.
Data authentication is a complex network communication mechanism that maintains non-repudiation and data integrity. Common data authentication methods include:
Password authentication
Users must enter a password to gain access to the data, which keeps the data safe from unauthorized access. Complex passwords using a combination of numbers, letters and special characters are used for more secure data and to further reduce risk.
This is just the first step in ensuring protection against cyber attacks using data encryption for cloud security.
Two-factor authentication
Aone-time password(OTP) is sent to the user’s cell phone number or e-mail address. If you are the original user, access to the data is approved after this OTP is entered.
Hackers trying to gain access will not have this OTP, which means that access to the data is denied and the account is temporarily locked to save the data from attacks.
Token authentication
A token is sent to the network server for authentication. The server checks the device credentials and approves or denies authentication.
Parity bit check
This strong and commonly used technique is also known ascyclic redundancycheck (CRC) and guarantees accurate data transmission.
A CRC code is added to the end of the data message before transmission. At the destination point, the receiver obtains the data with the CRC code and compares it with the original code. If the values are equal, the data was received correctly.
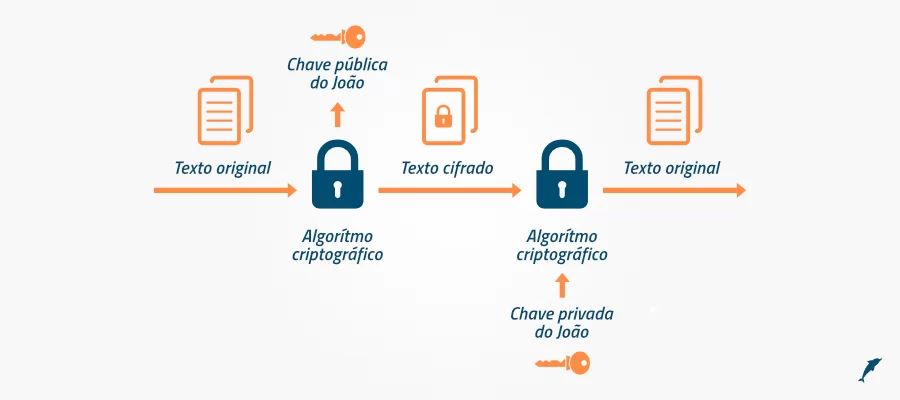
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates provide data encryption using specific algorithms. These certificates ensure the security of data transmission from malicious activities and third-party software.
Two types of mechanisms are used to encrypt the certificates: a public key and a private key.
The public key is recognized by the server and encrypts the data. SSL keeps data encrypted until the user completes the communication process. Data can only be decrypted by the private key.
If a hacker manages to hack the data during the communication process, the encryption will render the data useless. SSL is recommended as an international standard for secure data transmission on websites.
Best practices to protect against cyber attacks using data encryption
Organizations can employ several proven approaches to protect their data when using data encryption for cloud security. They include:
- Develop an encryption key and access management plan to ensure that data is decrypted when access to the data is required. Key management processes should be in place to prevent unauthorized disclosure of data or irrecoverable loss of important data;
- Ensure that encryption mechanisms comply with applicable laws and regulations. Any sharing of encrypted data, export or import of data encryption products (e.g. source code, software or technology) must comply with the applicable laws and regulations of the countries involved;
- Define data access levels. Monitor and record inappropriate access activities to reduce insider threat occurrences. Delete the accounts of former employees immediately after separation from the company;
- Train all staff in handling sensitive data using the latest technology and make sure they understand how systems use this information.
Data encryption for cloud security: mistakes your business should avoid
The biggest misconception about cybersecurity is that companies think they are completely protected from attacks because they have made large investments implementing security protocols.
They forget that there are always vulnerabilities that leave them exposed to risks, which can result in irrecoverable damage. With the advent of cloud storage, many companies have been led to believe that simply moving to the cloud guarantees protection against cyber attacks.
And while it is certainly a safe place to store a company’s sensitive data, it is not an impenetrable fortress, hence the importance of data encryption for cloud security.
In addition, some companies remain with older technologies without upgrading to newer, more secure advances, which leaves them still vulnerable to security risks.
Companies can leverage innovative security aspects to help them mitigate security threats. Software-defined networks can provide automated security at the hardware level through routers and switches.
Configuration management tools provide a convenient method to manage and automate security settings.
It is time for companies investing in cloud computing systems to also invest in making their cyber security systems more secure, reliable and robust against cyber attacks with the use of data encryption.
About Eval
EVAL has been developing projects in the financial, health, education and industry segments for more than 18 years. Since 2004, we have been offering solutions for Authentication, Electronic and Digital Signature and Protection Against Cyber Attacks. Currently, we are present in the main Brazilian banks, health institutions, schools and universities, and different industries.
With value recognized by the market, EVAL’s solutions and services meet the highest regulatory standards of public and private organizations, such as SBIS, ITI, PCI DSS, and LGPD. In practice, we promote information security and compliance, increase companies’ operational efficiency, and reduce costs.
Innovate now, lead always: get to know Eval’s solutions and services and take your company to the next level.
Eval, safety is value.